Netbackup 7.7.2 VTL Configuration:
Netbackup admin console, start the configure storage devices wizard.
Select the Media server name, which server to auto discover the tape library.
Now it detects one robo and tape drive automatically.
Now you can see the backup devices which discovered.
Verify or Modify the device configuration.
Once the config changes applied, then automatically restart the ltid (Media Manager service) automatically.
Now create a storage unit with the type of Media Manager.
Now successfully device was configured.
List and check the storage unit details.
List the drive status and details.
List the robo information.
Now inventory the volumes which is present in the tape library.
Select the Media server and Robo and start the inventory.
You can see the available tapes with the barcode.
Then, create a volume pool.
Create a volume and add to the volume pool.
List and check the volume details.
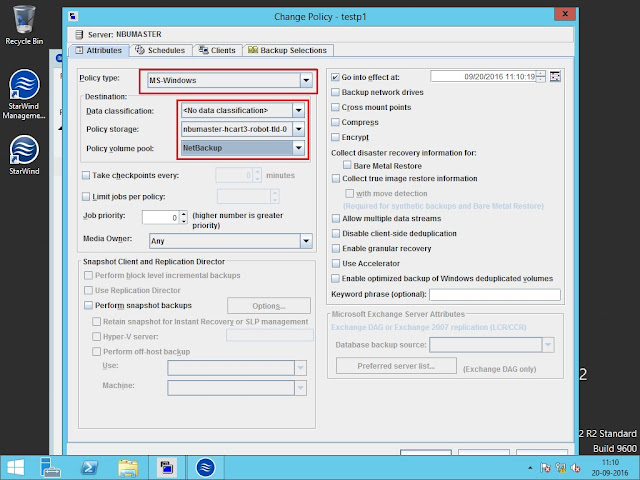
Now create a policy.
Select the policy type and storage unit.
Set the schedule type and backup window duration.
Add the clients.
Select the backup source path.
Run a manual backup to test.
Backup is active.
Test to restore the contents from the tape.
Netbackup admin console, start the configure storage devices wizard.
Select the Media server name, which server to auto discover the tape library.
Now it detects one robo and tape drive automatically.
Now you can see the backup devices which discovered.
Verify or Modify the device configuration.
Once the config changes applied, then automatically restart the ltid (Media Manager service) automatically.
Now create a storage unit with the type of Media Manager.
Now successfully device was configured.
List and check the storage unit details.
List the drive status and details.
List the robo information.
Now inventory the volumes which is present in the tape library.
Select the Media server and Robo and start the inventory.
You can see the available tapes with the barcode.
Then, create a volume pool.
Create a volume and add to the volume pool.
List and check the volume details.
Now create a policy.
Select the policy type and storage unit.
Set the schedule type and backup window duration.
Add the clients.
Select the backup source path.
Run a manual backup to test.
Backup is active.
Test to restore the contents from the tape.