What is NVMe?
NVM Express (NVMe) is a
data storage protocol that delivers the fastest response times for
business-critical enterprise applications. However, NVMe is more than a storage
specification; the broader NVMe over Fabrics protocol encompasses the entire
data path, from server to network to storage system.
NVMe—the NVM Express data storage
standard—is emerging as a core technology for enterprises that are building new
storage infrastructures or upgrading to modern ones.
NVMe is both a protocol
optimized for solid-state storage devices, and a set of open-source architectural
standards for NVMEM components and systems.
NVMe adds some new names for some common
structures.
An NVMe Qualified Name
(NQN) identifies an endpoint and is similar to an iSCSI Qualified Name (IQN) in
both format (domain registration date, domain registered, and something unique
like a serial number). A namespace is analogous to a LUN (Logical Unit Number,
a unique identifier for a logical or physical device); both represent an array
of blocks presented to an initiator. A subsystem is analogous to an initiator
group (igroup) (subsystems have considerably more functionality but for our
purposes, we are focusing on how to map LUNs/namespaces), it is used to mask an
initiator so that it can see and mount a LUN or namespace. Asymmetric Namespace
Access (ANA) is a new protocol feature for monitoring and communicating path
states to the host operating system’s Multipath I/O (MPIO) or multipath stack,
which uses information communicated through ANA to select and manage multiple
paths between the initiator and target.
NVMe will become an
essential part of the modern data center, because it addresses three crucial
attributes of data storage performance: IOPS,
throughput, and latency.
The IOPS and bandwidth improvements are
primarily the result of NVMe’s flexibility and its ability to take advantage of
fast transport technologies to move NVMe commands and data.
These transports include:
•
FCP. Currently available in speeds of 16 and
32Gbps and soon 64Gbps.
•
RDMA Protocol.
Data center fast Ethernet:
Currently available in 25, 40, 50, and 100Gbps.
InfiniBand: currently available
with speeds up to 100Gbps.
•
PCI Express 3.0. Supports 8 gigatransfers per second
(GT/s), which translates to approximately 6.4Gbps.
NVMe accelerates many of
today’s most important emergent business workloads:
Artificial
intelligence (AI).
Machine
learning (ML)/deep learning (DL).
Internet of Things (IoT).
NVMe as a Storage Attachment Architecture
NVMe
is most commonly used today for attaching disks and disk shelves. Many storage
vendors and suppliers have introduced offerings based on using NVMe as a
storage-attachment architecture and standard. Technically, in most cases, NVMe
is the protocol used to perform I/O, whereas the physical transport is
primarily PCIe.
In
this scenario, NVMe replaces the SCSI command set with the NVMe command set and
frequently replaces SATA or serial-attached SCSI (SAS) with PCIe to connect
drives to the storage controller. NVMe relies on a physical attachment and
transport. It uses PCIe as the transport.
NVMe-attached
flash offers more bandwidth and reduced latencies because:
•
It offers more and much deeper queues: 64k (65,535) queues, each
with a queue depth of 64k.
•
The NVMe command set is streamlined and therefore more efficient
than legacy SCSI command sets.
Create a dedicated NVMe protocol supported SVM.
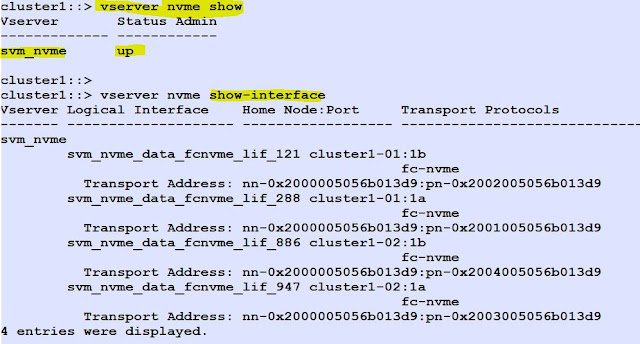
List the SVM details.
Check and List the NVMe/FC adapters.
Create NVMe LIF's.
List the NVMe Interfaces with their transport address.
Create a subsystem.
Get the host nqn (In linux host server:# cat /etc/nvme/hostnqn) & add the host nqn to subsystem.
Create a Namespace (like LUN).
Then Map the Namespace to the subsystem.
You can view the namespaces in ONTAP System Manager.
You can view NVMe Namespaces health and Performance in ActiveIQ Unified Manager.
Statistics view in sysstat command.
To list the enabled NVMe feature and Max. Nmaespace size.
Host Side Commands: (Linux Server)
To list the host nqn value.
# cat /etc/nvme/hostnqn
Check nvme-cli RPM or else install the RPM.
rpm -qa|grep nvme-cli
nvme-cli-1.6-1.el7.x86_64
To discover the namespaces (Devices).
# nvme connect-all --transport=fc
--traddr=nn-0x200a00a098c80f09:pn-0x200b00a098c80f09 --host-traddr=nn-0x20000090fae0ec9d:pn-0x10000090fae0ec9d
List the connected nvme devices.
nvme list